What is a Holistic Dentist?

When most people hear the term “Holistic Dentistry”, they start picturing lava lamps and healing crystals . . . there may also be some of you who may not even know what the word “holistic” means.
And there’s no shame in that!
This chapter was created to answer, in detail, “What is holistic or biological dentistry?” (and what it isn’t). Along the way, I’ll be clearing up major misconceptions and helping you understand the true meaning of holistic dentistry or biological dentistry.
Holistic Dentistry vs. Conventional Dentistry
First, let’s start with what you’re probably most familiar with already: contemporary clinical dentistry. You visit the general dentists’ office every six months, they polish your teeth, scrape the crusty stuff off, and tell you to wait for the dentist to complete their cursory exam.
You’re told about the cavities that need to be filled, the teeth that need “crowns” (or perhaps even “root canals”), and other news that you were already dreading on the drive over.

As you prepare to leave, you’re given a toothbrush and floss, maybe told to use the floss a little more often, and scheduled for another “cleaning” appointment in six months.
Traditional Dentistry = Disconnected Dentistry
If you take a look at the traditional six-month dental visit from an outside perspective, things start to look a bit strange, right?
What’s actually been solved during this routine visit, other than a mix of guilt and dread? You also probably feel powerless and unable to control what happens in your mouth and the impacts of your oral health on your long-term health.
Unfortunately, dentistry has followed a similar sobering trend of modern medicine.
You need an ENT for ear problems, an OB/GYN for women’s problems, a dentist for tooth problems—there is a doctor for every little part and piece of our bodies.
Somehow we’ve forgotten about whole body health—that everything is connected!
The other big obsession in Western medicine and dentistry is focusing on symptoms while completely disregarding the source or cause of the problem.
With traditional dentists who don’t take a holistic approach to dental care, you’ll hardly ever hear (or have time to ask) the following questions at your appointment:
Why did you get that cavity?
Do cavities have anything to do with what you eat or if you are getting enough nutrients from your food?
Do your hormones affect your teeth?
How long is that filling or crown going to last and what is it doing to your tooth and body?
These are extremely important questions because they affect your entire body, not just your teeth.
Thankfully, there IS a dentist who is able and ready to answer each of these questions – as well as any other health-related question you’ve been too afraid to ask your dentist.
Want to learn more about Holistic Dentistry? Click here to get a copy of my book, Healthy Mouth, Healthy You.
So What Is Holistic Dentistry or Biological Dentistry?
A holistic dentists (or biologic dentist) answer key questions concerning your overall health by focusing on the treatment of the whole person, rather than just the symptoms of dental disease.
Now, you may be wondering why a dentist, holistic or not, is qualified enough to consult with you on the health of your entire body. Here’s a statistic that may surprise you.
Renowned German Physician Dr. Reinhard Voll estimated that Nearly 80% of all illnesses are related entirely or partially to problems in the mouth.
Your biological dentist should be one of the first people you want to go to in matters of overall physical health, wellness, dental care, and whole-body health.
What separates holistic dentists from conventional dentists is that holistic dentists or biological dentists have dedicated their life’s work—and devoted their training—to learning how to treat their patients from an overall health perspective.
Understanding Holistic Dentistry and the Whole-Body Connection
Believe it or not, some of the most outspoken doctors about oral medicine and this tooth-body connection are cardiologists and doctors who work in cancer centers.
Dr. Thomas Levy, MD, JD has written a book in 2017 titled “The Hidden Epidemic.” It is full of long-standing scientific research pointing to the overwhelming health effects of dental infection.
One of his key takeaways includes the incredibly long (and deadly) list of diseases that have been shown to be connected to dental issues…
Heart Disease
Alzheimer’s disease
Anemia
Diabetes
High Blood Pressure
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Metabolic Syndrome
Osteoporosis
Pregnancy complications
Prostatitis
Pulmonary disease
Hearing loss
…and many more.
I am always sad to hear that patients don’t get this information about their oral health from their cancer doctors, heart doctors, or even their previous dentist!
Why aren’t more health professionals and dentists talking about this with you?
Most have been trained to think of dental conditions as a mouth-only problem and to treat them in a mechanical “drill-and-fill” method.
Most have not been trained to look for the source or root cause of problems or to look deeper into how dental problems can affect the rest of the body.
What Are Holistic Dentists and What's The Missing Link In Traditional Dental Training?
Like most other graduate schools, the training received in dental school is basic and very traditional.
The schools make sure their students can perform dental procedures before they graduate, including being able to…
diagnose dental problems
clean teeth
fill teeth
crown teeth
root canal teeth
pull teeth
perform dental surgery
place dental implants
…and replace teeth.
Some traditional dentists never complete another day of training after dental school, so their practices are centered on what they were taught – traditional dental treatments or just“fixing” teeth.
Here’s the *key* missing link in traditional dentistry. The dentist must choose to invest time and money into learning about whole-body treatments, including alternative methods and new approaches.
If you are looking for a dentist like this who will do more than just fix your teeth, there are certain things to look for. Read the list below to learn what to look for when searching for a holistic dental provider.
How Can You Find a Holistic Dentist or Biological Dentist?
Here is the ten-question checklist you should go through when choosing your first, or next, Dentist:
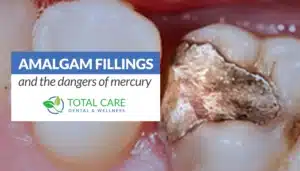
1 – Is it a “Mercury Free” and “Mercury safe” Dental Practice?
These are two different things. “Mercury Free” simply means the dentist does not place mercury-containing fillings (dental amalgam fillings), and thankfully, while it wasn’t always this way, quite a few dentists fall into this category now.
“Mercury safe” means that all mercury is handled safely and when removing old mercury fillings, you and the dental team will be protected. Make sure that the holistic dentist or biological dentist is MERCURY SAFE!

2 – Do They Have a Special Protocol for Removing Mercury Fillings?
To handle mercury fillings safely, the holistic dental office should have a mercury removal protocol including physical protection for you and the dental team during removal.
This should include a rubber dam, high-volume suction, and skin and airway protection, amongst other things.
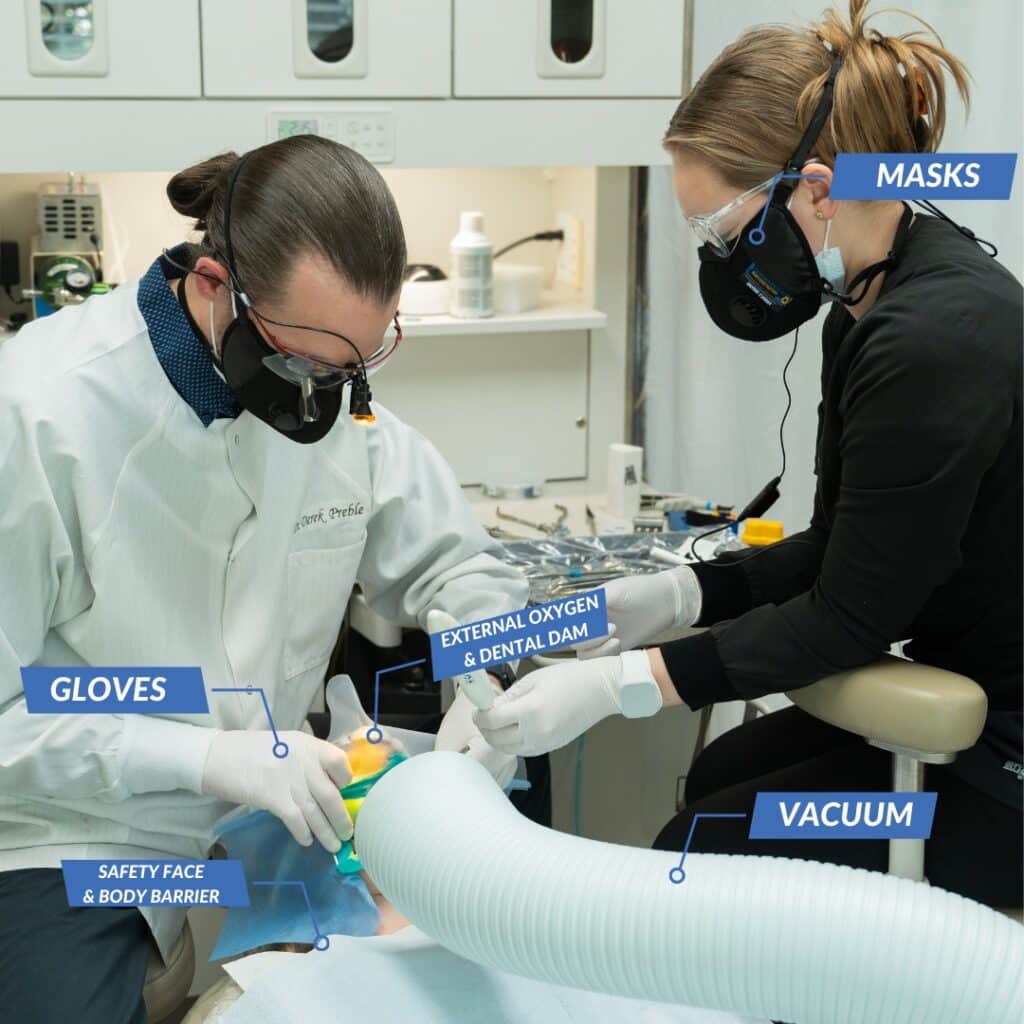

The office should also have a protocol for you to follow nutritionally to prepare your body to excrete the metals after removal.
Don’t be afraid to ask about these safety precautions upfront. If they are a holistic or biological dentist, they shouldn’t even bat an eye at your request.
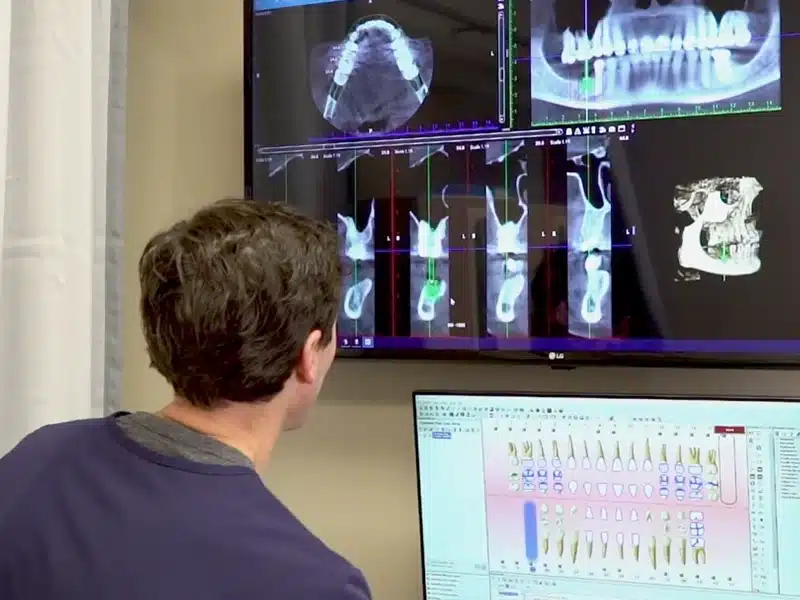
3 – Do They Use Digital X-rays and a CBCT?
X-rays have been and will continue to be, a concern in medicine and dentistry, but they are safer now than ever before. With the introduction of digital X-rays, the radiation used for an X-ray is dramatically reduced. X-rays are essential to proper diagnosis, but should only be done digitally to keep you safe.
A Cone Beam Tomography Scan (CBCT) is the next level of imaging that allows natural dentists to diagnose dental problems that may have been missed using a conventional dental X-ray. Some of the dental problems diagnosed with a CBCT include:
Cavitations
Sinus Perforations
Tooth Abscesses
Not every biological dentist has a CBCT in their office, but personally, I wouldn’t practice without it.
4 – What is Their Position on Fluoride?
Fluoride has had a controversial journey. It does make a tooth stronger—however, there are very undesirable side effects of fluoride on other areas of the body that are often ignored.

Fluoride should be used sparingly, if at all, and never ingested.
Whenever possible, a fluoride-free dental material alternative should be used. My Fluoride-free toothpowder and mouth rinse are good examples of safe and natural alternatives to traditional dental products that have ingredients that work as well as fluoride without any of the negative side effects.
Biological dentists across the country are now recommending fluoride-free dental products to their patients.
5 – Do They Address Nutrition in Relation to Dental Health?
The dentist has probably talked to you about not eating sugar—but that is just the tip of the nutritional iceberg when it comes to your dental health.
Nutrition can hurt or heal your teeth, bone, and gums.
Holistic dentists or Biological dentists should be able to guide you to a Mouth-Friendly diet.
6 – What is their position on root canals?
Root canals save teeth—in the short term. Their effect on health in the long term is the real problem.
A very educated and honest approach to root canals, as well as high-tech diagnostic tools like Cone Beam CT scanners, are necessary to really take care of your oral health and help you avoid a root canal if at all possible
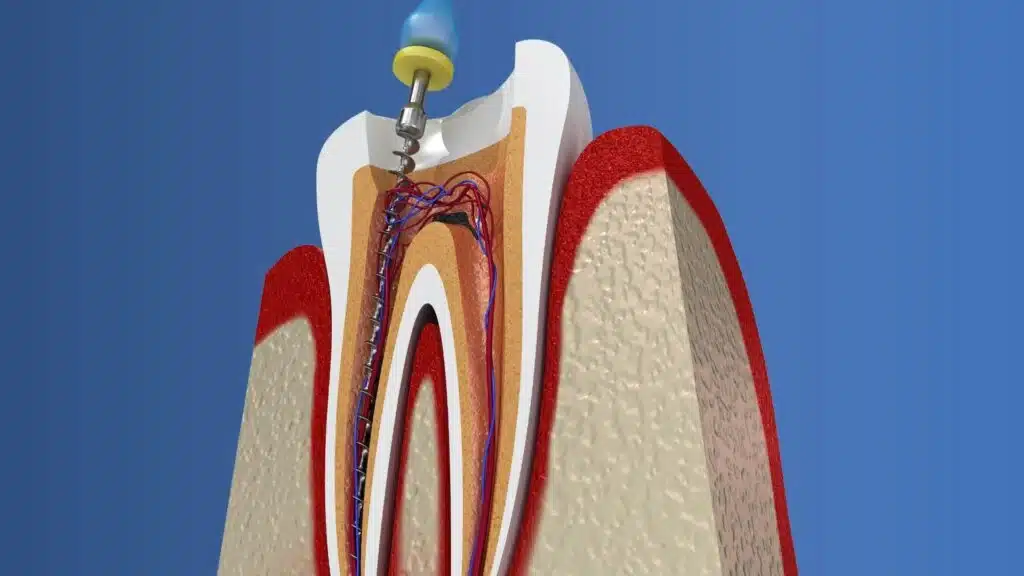
7 – Do They Place Biomimetic Dental Restorations?
Biomimetic is just a fancy word for “mimics nature”.
No dental restoration is as good as what you were born with . . . but some are closer to nature than others. A holistic dentist or biomimetic dentist should be able to provide bio-mimetic tooth restoration solutions using biocompatible materials.
If you need a dental restoration, make sure it will help preserve and protect your tooth, not just provide a temporary fix.
8 – Do They Have Non-Toxic Recommendations for Dental Products?
As a practicing dentist, I get boxes of toothpaste for free from dental product manufacturers. It is free to give to patients—but I don’t do it.
Why? Because I don’t recommend many of the ingredients in those products, and neither should any holistic dentist you visit. They should have well-researched alternatives to traditional dental products available for you.
9 – Do They Use a Laser to Diagnose Dental Cavities?
Are you used to your traditional dentist “poking” a tooth to see if you have tooth decay? Unfortunately, the poking method (something I was taught in school) is only 25% accurate. That means any dentist this is only using this diagnostic method is missing 75% of the cavities while they are still small (and easily healed or treated).
Now, there is a specialized laser that detects cavities—and it is 90% accurate in diagnosis.
Make sure you look for a biological dentist or natural dentist that has these new technologies and knows how to use them in order to help keep you healthy.
10 – What is Their Position on Tooth Remineralization?
There is a lot of outrage on both sides about “healing teeth”
Is it possible? Have dentists been lying about the ability to heal cavities naturally all this time?
There is a truth to this controversy, but the reality lies somewhere in the middle of the conversation. It is possible to remineralize teeth, but It is possible to remineralize teeth, but it’s important to talk about which areas of tooth decay will predictably remineralize. Make sure your dental office has a protocol to remineralize teeth, and take time to discuss it with you.
When considering your options of visiting a holistic dentist v.s. a traditional dentist, you should consider how much the dentist will be looking out for your overall health.

Calculate Your Results
When using the ten-question mental checklist above, the holistic dentist or biological dentist should score at least SEVEN OUT OF TEN.
That is how you will know that they are really whole-body and health-focused and that they will continue to commit themselves to learning and mastering cutting-edge alternative and holistic methods.
What is the key to all of this?
DON’T SETTLE FOR LESS.
With so many incredible holistic dentists and biological dentists out there, you shouldn’t have to settle. You can find a holistic dentist HERE on my Living Well online directory. I’ve been networking and trying to find the best holistic dentists in the country so I can provide this resource to patients seeking an office with holistic dental care.
Now that we’ve answered the question “What is a holistic dentist?” let’s get back to some of the basics that will help you best care for your teeth.
In Chapter 2 we’re going to discuss what actually causes cavities (Hint – it’s not just sugar!)
Schedule Your New Patient Exam With Total Care Dental & Wellness
With a comprehensive exam, you’ll receive:
- A low dose cone beam 3d Dental Xray (CBCT)
- Tooth Xrays
- Dental photographs
- A comprehensive gum exam with an intraoral scan
- A comprehensive oral exam by a Total Care Doctor
- Jaw joint exam
- Oxygen, Sleep, and Airway Evaluation
You will leave the appointment with a report of findings and treatment recommendations from your doctor and care coordinator. Finances, scheduling, and other instructions will also be provided.